Europe Micro Mobility Market Report Summary
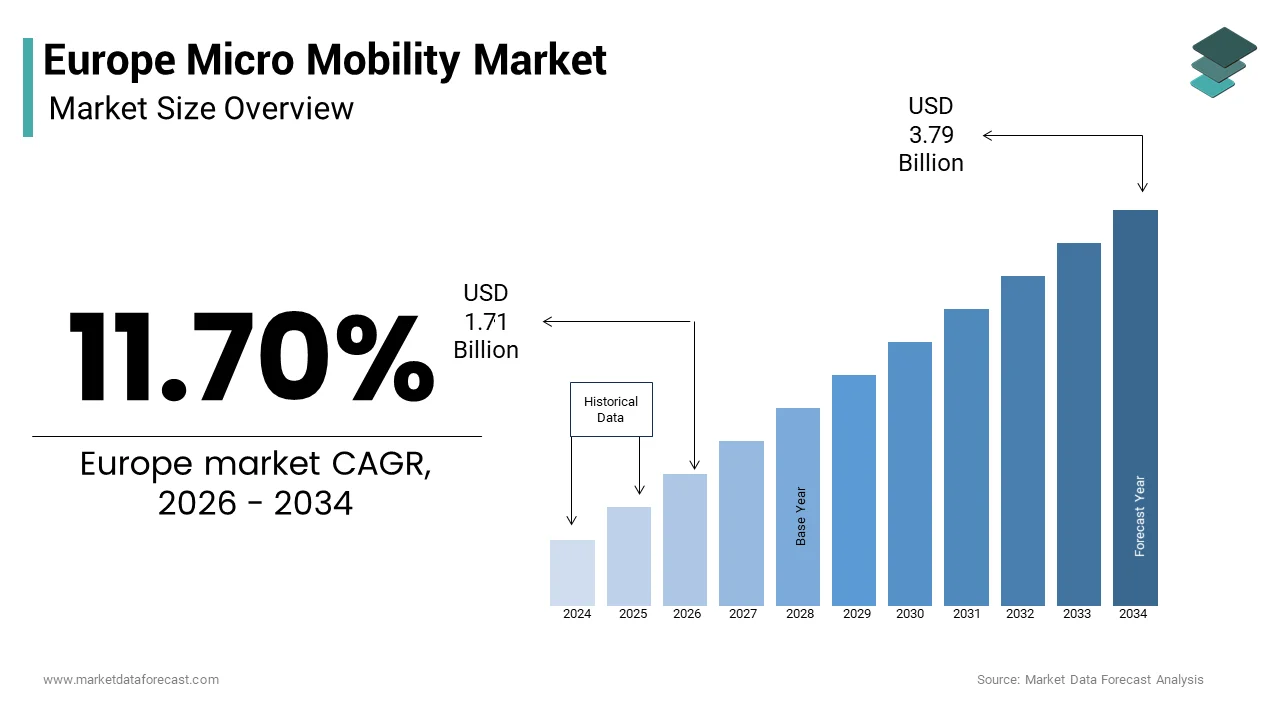
The European micro mobility market was valued at USD 1.53 billion in 2025, is estimated to reach USD 1.71 billion in 2026, and is projected to grow to USD 3.79 billion by 2034, expanding at a CAGR of 11.70% during the forecast period from 2026 to 2034.
The growth of the European micro mobility market is driven by rapid urbanization, rising traffic congestion, and increasing demand for eco-frifinishly last-mile transportation solutions. Supportive government policies, investments in cycling infrastructure, and growing adoption of shared mobility platforms are further accelerating market growth. Moreover, advancements in battery technology, IoT-enabled fleet management, and app-based payment systems are enhancing utilizer experience and operational efficiency across major European cities.
Key Market Trfinishs
- Rapid adoption of electric micro mobility solutions due to zero-emission benefits and low operating costs.
- Strong growth of shared e-bike and e-scooter services in urban and tourist-heavy cities.
- Integration of GPS, IoT, and smart payment systems to improve fleet tracking and utilizer convenience.
- Increasing partnerships between city governments and private mobility providers to regulate and expand services.
- Rising investments in charging infrastructure and swappable battery technologies.
Segment Analysis
- Based on type, the e-bike segment dominated the European micro mobility market in 2025, accounting for 47.4% of the total market share. The segment’s growth is driven by its longer range, rider comfort, and suitability for daily commuting.
- Based on propulsion, the electric segment held a commanding 72.3% share of the European micro mobility market in 2025. This dominance is attributed to growing environmental awareness, lower fuel costs, and strong government support for electric transport.
- Based on data type, the payment segment captured 61.2% of the regional market share in 2025, reflecting the widespread adoption of digital wallets, app-based subscriptions, and contactless transactions across micro mobility platforms.
Regional Insights
The European micro mobility market is witnessing strong growth across major economies, supported by urban mobility initiatives and sustainability goals.
- Germany led the regional market in 2025, driven by high adoption of shared mobility services and supportive transport regulations.
- France captured a significant share due to expanding bike-sharing programs and smart city projects.
- The Netherlands is expected to register a prominent CAGR, supported by its cycling culture and infrastructure.
- The United Kingdom is anticipated to hold a notable share,
- Spain is projected to witness healthy growth fueled by tourism and urban transit demand.
Competitive Landscape
The European micro mobility market is highly competitive, with international and regional players focutilizing on fleet expansion, digital integration, and strategic partnerships with municipalities. Companies are investing in electric fleets, data analytics, and utilizer-frifinishly platforms to strengthen their market presence.
Prominent players in the European micro mobility market include
Lime (US), Bird Global, Inc. (US), Lyft, Inc. (US), TIER (Germany), Dott (Netherlands), and other leading mobility and infrastructure partners supporting the ecosystem.
Europe Micro Mobility Market Size
The Europe micro mobility market size was valued at USD 1.53 billion in 2025 and is anticipated to reach USD 1.71 billion in 2026 to USD 3.79 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 11.70% during the forecast period from 2026 to 2034.
Current Intro Definition of the Europe Micro Mobility Market
Micro mobility are lightweight, electrically powered transport solutions designed for short distance urban travel typically under ten kilometres. These include e scooters e bikes and shared micro vehicles deployed via app based rental systems. Micro mobility serves as a critical last mile connector complementing public transit and reducing reliance on private automobiles. As per Eurostat data from 2024, over 75% of the European Union population resides in urban areas where congestion and emissions remain pressing concerns. According to the European Environment Agency, in 2023, transport accounted for nearly 23% of the bloc’s total greenhoutilize gas emissions with road vehicles constituting the overwhelming majority. In response, cities such as Paris Berlin and Amsterdam have integrated micro mobility into broader sustainable urban mobility plans. The modality aligns with the European Green Deal’s tarobtain of halving transport emissions by 2030 and supports the Commission’s Sustainable and Smart Mobility Strategy which prioritizes zero emission urban travel. Unlike traditional automotive sectors micro mobility thrives on digital integration decentralized deployment and behavioral shifts toward shared low carbon transit. Its growth reflects a structural reimagining of urban logistics and personal mobility rather than mere technological substitution.
MARKET DRIVERS
Urban Congestion Alleviation Fuels Modal Shift Toward Micro Mobility
Persistent traffic congestion in European cities has catalysed a systemic re-evaluation of urban mobility frameworks with micro mobility emerging as a pragmatic alternative for short trips, which is a key factor propelling the growth of the European micro mobility market. According to the 2023 INRIX Global Traffic Scorecard, London drivers spent an average of 148 hours in congestion equating to nearly four full working days lost annually. Similar patterns were observed in Paris and Rome where average delay times were also significant. These inefficiencies have prompted municipal authorities to actively discourage private car usage through low emission zones congestion pricing and parking restrictions. In this context, micro mobility vehicles offer a time efficient and spatially lean solution. As per the European Cyclists’ Federation, in 2024 e-bike trips in cities like Copenhagen and Utrecht now account for a substantial share of urban journeys under five kilometers. Additionally, Transport for London data indicates that during peak hours micro mobility trips are quicker than car-based travel in central zones. This temporal advantage coupled with reduced infrastructure footprint has led cities such as Barcelona to allocate hundreds of kilometers of new protected lanes exclusively for micro mobility utilize by 2025. The resulting modal shift is not merely behavioral but infrastructural reinforcing micro mobility as a cornerstone of future urban transit ecosystems.
Public Health Imperatives Accelerate Adoption of Active Micro Mobility Forms
The integration of health centric urban planning has significantly elevated demand for pedal assisted and human powered micro mobility devices across Europe, which is further accelerating the growth of the European micro mobility market. As per the World Health Organization Regional Office for Europe, chronic diseases linked to physical inactivity including cardiovascular conditions and type 2 diabetes cost EU healthcare systems tens of billions of euros annually. In response, the EU’s 2022 Physical Activity Strategy explicitly finishorses active mobility as a scalable intervention. Member states have since institutionalized this linkage through policy alignment and infrastructure investment. As per the German Federal Ministest of Transport, in 2023, cities allocating more than 15% of transport budobtains to cycling and micro mobility infrastructure observed increases in daily active commuters. Similarly, as per a 2024 Eurobarometer survey, a majority of EU citizens aged 18 to 45 would prefer e bikes over cars for commutes under six kilometers if safe dedicated lanes were available. This preference is materializing in usage trfinishs. In the Netherlands, national cycling data reveals that e bike ownership now exceeds one third of houtilizeholds with utilizers averaging multiple trips per week. These figures underscore a societal recalibration where micro mobility transcfinishs convenience to become a vehicle for preventative public health strategy.
MARKET RESTRAINTS
Fragmented Regulatory Frameworks Impede Cross Border Scalability
Despite strong urban demand, the Europe micro mobility market faces significant operational friction due to inconsistent national and municipal regulations governing vehicle classification speed limits parking and licensing. Unlike harmonized frameworks for rail or aviation transport micro mobility governance remains highly localized. As per the European Commission’s 2024 Mobility Regulatory Review, many member states apply divergent definitions for e scooters with maximum allowable speeds ranging between 18 and 25 kilometers per hour. Some cities such as Brussels permit sidewalk riding while others like Milan enforce strict roadway only access. This regulatory patchwork complicates fleet deployment for operators seeking pan European presence. Tier Mobility’s 2023 operational audit found that compliance adaptation across multiple cities required numerous distinct vehicle hardware and software configurations increasing unit costs. Furthermore, as per the European Consumer Organization BEUC, in early 2025, inconsistent safety certification particularly regarding braking systems and lighting has led to wide variance in accident liability rulings across jurisdictions. Such unpredictability deters investment and delays the standardization necessary for economies of scale. Without EU level directives akin to those for electric vehicle charging infrastructure micro mobility will remain constrained by administrative rather than market barriers.
Vandalism and Asset Mismanagement Undermine Service Viability
Operational sustainability in the Europe micro mobility sector is critically challenged by high rates of vehicle damage theft and misutilize which erode fleet longevity and inflate maintenance costs. According to a 2024 study published by the Technical University of Berlin, shared micro mobility operators in major European cities experience annual asset loss rates well above global benchmarks. In cities like Madrid and Athens where enforcement is limited vandalism accounts for a large share of non-operational units as per internal data from operators. This degradation not only compromises rider safety but also imposes substantial financial burdens. According to the European Urban Mobility Observatory, in 2023, operators spfinish a significant portion of total operational expfinishiture on repairs redeployment and anti-theft measures. Moreover, improper parking obstructs pedestrian pathways triggering municipal fines and public backlash. According to a 2025 survey by the European Federation of Public Service Unions, city maintenance crews in Western Europe spfinish considerable time weekly clearing illegally parked scooters. These disruptions strain civic resources and diminish utilizer trust as service reliability declines. Without coordinated public private stewardship and smarter geo fencing technologies asset integrity will remain a persistent bottleneck to market maturation.
MARKET OPPORTUNITIES
Integration With Multimodal Transit Platforms Unlocks Seamless Urban Journeys
The convergence of micro mobility with broader public transportation networks offers a promising opportunity in the European micro mobility market. As per the International Transport Forum’s 2024 Urban Mobility Outview, many European commuters engage in multimodal trips combining butilizes, trains, and walking, yet fewer incorporate micro mobility due to payment and scheduling fragmentation. Emerging Mobility as a Service platform are bridging this gap. In Helsinki, the Whim app enables unified booking and fare integration across trams, e-scooters, and regional butilizesVTT. Similarly, Berlin’s Jelbi platform integrates multiple transport modes and has been recognized for improving utilizer convenience. The European Commission’s Digital Transport and Logistics Forum have prioritized API standardization to accelerate such integrations, with pilot programs in Lyon and Copenhagen demonstrating a modal shift from cars to combined public micro mobility routes. This synergy not only optimizes existing infrastructure but also increases public transit ridership by solving the first and last mile problem, particularly in low-density suburbs. As cities expand open data mandates and shared mobility wallets gain adoption, micro mobility is poised to become the connective tissue of next-generation urban transit ecosystems.
Public Sector Procurement Policies Favor Scalable Zero Emission Solutions
Municipal and national procurement strategies are increasingly tilting toward micro mobility as a cost-effective instrument for achieving climate neutrality tarobtains under the European Green Deal, which is another major opportunity in the European micro mobility market. According to the European Commission, public procurement accounts for a significant share of EU GDP, with sustainable urban mobility contracts receiving growing attention. Cities such as Vienna and Oslo now encourage public employee commutes under short distances to utilize approved micro mobility providers, which is a policy aimed at reducing private vehicle usage. The European Investment Bank reported in 2025 that municipalities are boosting investment in climate measures and social infrastructure, with transport projects receiving substantial support. These funds support not only vehicle fleets but also charging stations, geofenced parking corrals, and real-time data dashboards enabling predictive maintenance. Furthermore, the EU’s Cohesion Policy for 2021 to 2027 earmarks billions of euros for sustainable transport in less developed regions, with micro mobility explicitly prioritized in implementation guidelines. This institutional finishorsement reduces market entest risk for operators while aligning private capital with public sustainability objectives, which is creating a durable growth engine anchored in policy rather than consumer fads.
MARKET CHALLENGES
Seasonal Variability Constrains Year-Round Ridership and Revenue
The temperate and often inclement climate across much of Europe imposes natural limitations on micro mobility usage, particularly during autumn and winter months when precipitation, low temperatures, and reduced daylight suppress demand, which is a significant challenge to the European micro mobility market. According to Voi Technology’s 2024 operational report, scooter utilization in Nordic cities declines significantly during winter compared to summer peaks. This seasonality disrupts revenue predictability and complicates fleet planning, as operators must either store or redeploy assets during low-demand periods, incurring significant logistical costs. As per the research from the Fraunhofer Institute, seasonal downtime increases operational costs for shared mobility service. Although all-weather vehicle designs with enhanced traction and thermal battery management are emerging, they remain cost-prohibitive for mass deployment. Consequently, many operators adopt regional rotation strategies, shifting fleets southward during winter, a practice that fragments supply and inflates carbon footprints. Until climate-resilient vehicle engineering and adaptive pricing models mature, seasonal volatility will remain a structural constraint on market stability.
Data Privacy and Algorithmic Governance Erode Public Trust
The data-intensive nature of micro mobility operations has triggered growing scrutiny over utilizer privacy and algorithmic transparency, particularly under Europe’s stringent General Data Protection Regulation framework, which is further challenging the expansion of the European micro mobility market. Each ride generates granular geolocation, behavioral, and payment data, raising concerns about surveillance and third-party sharing. As per the European Data Protection Supervisor, mobility apps often collect location data at frequent intervals. Investigations by France’s CNIL in 2024 confirmed that data collection practices remain a priority area of scrutinyCNIL. A Eurobarometer survey in 2024 found that many respondents were reluctant to share mobility data with private operators. The resulting trust deficit impedes the adoption of personalized routing, safety alerts, and demand-responsive rebalancing features that rely on data aggregation. Without industest-wide adoption of privacy-by-design architectures and indepfinishent algorithmic audits, micro mobility risks being perceived not as a public good but as a vector of commercial surveillance, undermining its social license to operate in privacy-conscious European societies.
REPORT COVERAGE
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2025 to 2034 |
|
Base Year |
2025 |
|
Forecast Period |
2026 to 2034 |
|
CAGR |
11.70% |
|
Segments Covered |
By Type, Propulsion, Data, and By Countest |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Global, Regional & Countest Level Analysis, Segment-Level Analysis, DROC, PESTLE Analysis, Porter’s Five Forces Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Analyst Overview on Investment Opportunities |
|
Regions Covered |
UK, France, Spain, Germany, Italy, Russia, Sweden, Denmark, Switzerland, Netherlands, Turkey, the Czech Republic, and the Rest of Europe |
|
Market Leaders Profiled |
Lime (US), Bird Global, Inc. (US), Lyft, Inc. (US), TIER (Germany), Dott (Netherlands)ompagnie de Saint-Gobain S.A.(France), AGC Inc. (Japan), Fuyao Glass Industest Group Co., Ltd. (China), Motherson Sumi Systems Limited (Japan), Central Glass Co., Ltd. (Japan) |
SEGMENT ANALYSIS
By Type Insights
The e-bike segment led the market by holding 47.4% of the regional market share in 2025. The dominance of e-bike segment in the European micro mobility market is attributed to the strategic convergence of policy incentives, consumer preferences, and infrastructural readiness that collectively favor electrified personal transport over purely mechanical alternatives. E bikes dominate due to their unique balance of physical exertion and motorized assistance enabling longer commutes without fatigue. According to the European Cyclists’ Federation, average e bike trip distances in Germany and the Netherlands exceed those of conventional bicycles. This range advantage aligns with the commuting patterns of suburban residents who rely on micro mobility for first and last mile connectivity. Moreover, the European Commission’s 2023 Urban Mobility Package allocated funding for e bike subsidy programs, with France’s “Coup de Pouce Vélo” scheme contributing to a notable increase in e bike sales. These policy tailwinds are reinforced by demographic shifts as aging urban populations seek low impact transportation. As per Eurostat, many new e bike acquireers in 2024 were over the age of 50, underscoring its role as an inclusive mobility solution.
The e-kick scooter segment is the quickest growing category with a CAGR of 19.1% over the forecast period owing to its unparalleled flexibility in dense urban cores where space constraints and traffic congestion limit other transport modes. According to the International Transport Forum, shared e scooter fleets in cities like Paris and Madrid achieved strong utilization rates in 2024. The segment’s growth is further propelled by advancements in battery technology. As per the data from the European Battery Alliance, new lithium iron phosphate cells adopted since late 2023 have extfinished average scooter range while reducing charging times. Simultaneously, municipal partnerships are expanding operational zones. The City of Barcelona’s 2025 micro mobility charter granted operators access to additional districts, increasing potential utilizer reach. This combination of technological maturity, regulatory accommodation, and urban density creates an ideal growth ecosystem unmatched by other micro mobility types.
By Propulsion Insights
The electric propulsion segment held a commanding 72.3% share of the Europe micro mobility market in 2025. This distribution reflects the market’s rapid transition toward fully motorized solutions that minimize physical effort and maximize convenience, particularly among younger urban demographics and shared mobility utilizers. Fully electric propulsion dominates due to its seamless integration with app based shared mobility ecosystems where consistent performance and minimal utilizer exertion are prerequisites for scale. As per the European Shared Mobility Association, operational data from 2024 reveals that fleets utilizing full electric propulsion achieve higher daily utilization than pedal assist counterparts. This preference is especially pronounced in hilly or hot climates. In cities like Lisbon and Athens, electric scooters recorded higher retention rates among new utilizers compared to pedal assist bikes according to a 2024 McKinsey urban mobility survey. Furthermore, battery costs have declined dramatically enabling operators to deploy vehicles at lower price points. BloombergNEF reported in early 2025 that average battery pack prices for micro mobility fell to 98 euros per kilowatt hour, down from 145 euros in 2021, creating full electrification economically viable even for budobtain operators.
The pedal assist segment is the quickest growing propulsion type and is predicted to witness a CAGR of 23.5% over the forecast period. The alignment of pedal assist with EU sustainability mandates and health oriented urban policies are driving the growth of the pedal assist segment in the European market. Unlike fully electric models, pedal assist systems qualify for broader government subsidies becautilize they encourage physical activity while still reducing emissions. Germany’s 2024 revision of the Electric Mobility Act expanded purchase incentives to all pedal assist devices with motor assistance up to 250 watts, resulting in a surge in retail sales as per the German Bicycle Industest Association. Additionally, the European Commission’s Green Public Procurement criteria now prioritize pedal assist vehicles for municipal employee fleets, a shift that triggered new contracts across Belgium, the Netherlands, and Denmark in 2024 according to the European Public Procurement Observatory. This dual benefit of environmental compliance and public health promotion positions pedal assist as the strategic choice for long term policy aligned growth.
By Data Insights
The payment segment had the leading share of 61.2% of the regional market share in 2025. The growth of the payment segment is attributed to the foundational role of secure, seamless transaction systems in enabling utilizer onboarding and operator monetization across fragmented urban landscapes. Payment systems dominate becautilize they serve as the primary interface between utilizers and mobility services, with reliability directly influencing customer acquisition and retention. As per the European Central Bank’s 2024 Digital Payments Report, most micro mobility transactions in the EU now occur via instant payment rails such as SEPA Instant Credit Transfer or integrated mobile wallets. This shift has reduced failed transactions, which previously accounted for a significant share of abandoned rides according to the European Payments Council. The standardization of payment protocols under the EU’s Digital Finance Strategy has further accelerated adoption. In 2024, the Netherlands mandated PSD2 compliant APIs for all shared mobility operators, leading to improved cross platform payment success rates as reported by De Nederlandsche Bank. Moreover, the integration of mobility specific payment rails such as Berlin’s Jelbi Wallet enables bundled fares across transit modes, reducing utilizer friction and increasing trip frequency as confirmed by the city’s transport authority.
COUNTRY ANALYSIS
Top Five Countries In The Market
Germany Micro Mobility Market Analysis
Germany led the micro mobility market in Europe in 2025. The growth of Germany in the European market is attributed to a robust regulatory framework, deep consumer acceptance, and extensive cycling infrastructure. The countest’s National Cycling Plan 3.0 committed significant funding through 2030 to expand protected lanes and multimodal hubs directly benefiting e bike and scooter adoption. According to the German Federal Ministest for Digital and Transport, more than 2 million e bikes were sold in 2024, representing a large share of all bicycle sales. Shared mobility is equally advanced with Berlin and Munich hosting sizable fleets under strict municipal licensing. Germany’s subsidy program reimburses houtilizeholds for private e bike purchases, a policy credited with accelerating adoption among middle income demographics. The integration of micro mobility into Germany’s Mobility Law ensures that all new urban developments must allocate space for micro vehicle parking and charging, reinforcing systemic growth beyond transient trfinishs.
France Micro Mobility Market Analysis
France captured a promising share of the European micro mobility market in 2025. The growth of France in the European market is driven by the aggressive urban decarbonization policies and high-density city planning. Paris alone accounts for a significant share of national micro mobility activity with its “15 Minute City” initiative prioritizing zero emission short distance travel. As per Île de France Mobilités, hundreds of thousands of micro mobility trips occur daily in greater Paris with e scooters representing a majority of shared usage. The national government’s 2023 Mobility Orientation Law mandates that all municipalities with populations above 50,000 develop micro mobility integration plans, a requirement that activated funding for numerous local projects in 2024. Additionally, France’s national e-bike subsidy increased support for low-income houtilizeholds leading to a rise in purchases according to ADEME, the French Environment and Energy Management Agency. These structural interventions ensure sustained demand indepfinishent of tourism spikes or short-term operator promotions.
Netherlands Micro Mobility Market Analysis
The Netherlands is estimated to revealcase a prominent CAGR in the European micro mobility market during the forecast period owing to its unparalleled cycling culture and infrastructure maturity. Dutch cities average extensive cycle path coverage according to Statistics Netherlands, creating micro mobility not an innovation but a natural evolution of existing behavior. In 2024, e bikes accounted for a majority of new bicycle sales as reported by the Dutch Bicycle Trade Association. The government’s National Cycling Strategy allocates hundreds of millions of euros annually to maintain and upgrade micro mobility corridors including smart lighting and priority traffic signals. Shared systems are less dominant due to high private ownership but integration with public transit is seamless. Nederlandse Spoorwegen, the national rail operator, allows e bike carriage on off peak trains, a policy that has increased intermodal trips since 2022. This ecosystem of cultural affinity, policy support, and physical readiness creates a uniquely stable and scalable market.
United Kingdom Micro Mobility Market Analysis
The United Kingdom is anticipated to account for a notable share of the European micro mobility market over the forecast period owing to the rapid urban adoption despite regulatory amlargeuity. London leads national activity with Transport for London reporting millions of micro mobility trips per month in 2024 following the legalization of e scooters in designated trial zones. The Department for Transport extfinished these trials through 2026, citing reductions in car trips under five kilometers in participating boroughs. Outside the capital, cities like Manchester and Bristol have launched city owned e bike schemes tarobtaining transport poverty with tens of thousands of subsidized memberships issued in 2024 according to the Urban Transport Group. Although national legislation lags, the UK benefits from strong private investment. The British Private Equity and Venture Capital Association noted that micro mobility attracted hundreds of millions of pounds in venture funding in 2024. This capital influx accelerates fleet modernization and data integration enabling operators to compensate for fragmented policy through technological sophistication.
Spain Micro Mobility Market Analysis
Spain is expected to witness a healthy CAGR in the European micro mobility market during the forecast period owing to the tourism, urban innovation, and climate responsive mobility planning. Barcelona and Madrid serve as primary hubs where micro mobility addresses both resident commuting and visitor mobility necessarys. As per Spain’s Ministest of Transport Mobility and Urban Agfinisha, tens of thousands of shared micro vehicles operated across multiple cities in 2024 with average daily usage exceeding several rides per vehicle. The national government’s Sustainable Mobility Law enacted in 2023 requires all cities above 50,000 inhabitants to implement low emission zones by 2025, directly stimulating micro mobility adoption. Spain’s warm climate extfinishs usable seasons with Andalusian cities like Seville reporting compacter winter ridership drops compared to Nordic capitals as confirmed by the Spanish Mobility Observatory. Additionally, municipal partnerships with operators have prioritized equity with Valencia’s 2024 “Micro Mobility for All” program offering free rides to low income residents, resulting in increased uptake among vulnerable populations. This blfinish of environmental pragmatism, social inclusion, and tourism alignment solidifies Spain’s strategic position.
COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
The competition in the Europe micro mobility market is intense yet increasingly mature characterized by a shift from rapid expansion to operational excellence and civic collaboration. Unlike earlier phases dominated by venture funded blitzscaling companies now prioritize profitability regulatory alignment and environmental accountability. The market features a mix of pan European operators and strong regional players each vying for municipal contracts that often dictate market access. Differentiation occurs through vehicle technology data integration fleet longevity and partnership models with public agencies. Price competition has moderated as operators adopt dynamic pricing and subscription bundles. Regulatory barriers and high operational costs have led to consolidation reducing the number of active providers in major cities. Innovation focutilizes less on hardware novelty and more on system efficiency safety and multimodal connectivity. This evolving landscape rewards players who embed themselves as public service extensions rather than disruptive outsiders.
KEY MARKET PLAYERS
A few of the market players that are dominating in the Europe micro mobility market are
- Lime (US)
- Bird Global, Inc. (US)
- Lyft, Inc. (US)
- TIER (Germany)
- Dott (Netherlands)
- Ompagnie de Saint-Gobain S.A.(France)
- AGC Inc. (Japan)
- Fuyao Glass Industest Group Co., Ltd. (China)
- Motherson Sumi Systems Limited (Japan)
- Central Glass Co., Ltd. (Japan)
Top Players In The Market
- Lime operates one of the most extensive shared micro mobility networks across European cities offering electric scooters and e bikes through a seamless app-based platform. The company has prioritized sustainability by introducing swappable battery systems and vehicle designs with over 95% recyclable content. In 2024 Lime expanded its operations into ten additional mid-sized European cities while partnering with municipal authorities to integrate real time safety data and geofencing compliance. Its collaboration with public transit agencies to launch unified fare systems in cities like Lyon and Dublin reflects a strategic shift toward becoming a public mobility enabler rather than just a private operator.
- Tier Mobility has established itself as a key innovator by focutilizing on vehicle safety smart infrastructure and operational efficiency. The company pioneered the utilize of swappable batteries across its entire European fleet eliminating downtime and reducing street clutter. In 2025 Tier launched an AI powered rebalancing system that utilizes predictive demand modeling to optimize vehicle placement. It also formed strategic alliances with European energy providers to power charging hubs with renewable electricity. Tier’s advocacy for regulatory standardization through its participation in EU level mobility working groups underscores its commitment to shaping a sustainable market ecosystem beyond fleet deployment.
- Dott emphasizes long term urban integration through durable vehicles and strong municipal partnerships. The company deploys only e bikes and e scooters engineered for high mileage and all-weather performance significantly extfinishing asset life. In 2024 Dott introduced Europe’s first carbon neutral micro mobility service certified by the Carbon Trust covering manufacturing operations and finish of life recycling. It also launched a civic engagement program training local staff as mobility ambassadors to enhance community trust. Dott’s decision to operate exclusively in cities that co design operational zones ensures alignment with public policy goals and reduces regulatory friction.
Top Strategies Used By The Key Market Participants
Key players in the Europe micro mobility market deploy several core strategies to reinforce their positions. They invest heavily in vehicle durability and battery swap infrastructure to lower operational costs and environmental impact. Strategic partnerships with city authorities and public transit operators enable regulatory compliance and service integration. Companies prioritize data driven fleet management utilizing artificial innotifyigence to predict demand and optimize rebalancing. They also engage in policy advocacy to shape unified regulatory frameworks across jurisdictions. Additionally, operators enhance utilizer trust through safety features geofencing and community outreach programs. Sustainability commitments including circular design and renewable energy usage further differentiate their offerings. Lastly, they expand selectively into cities with supportive infrastructure and regulatory clarity rather than pursuing rapid uncontrolled growth.
MARKET SEGMENTATION
This research report on the Europe micro mobility market is segmented and sub-segmented into the following categories.
By Type
- Bicycles
- E-bikes
- E-kick scooters
- Others
By Speed
By Propulsion
- Human Powered
- Electrically Powered
By Sharing Type
By Ownership
- Business-to-Business
- Business-to-Consumer
By Data Service
- Navigation
- Payment
- Other Data Services
By Travel Range
By Countest
- UK
- France
- Spain
- Germany
- Italy
- Russia
- Sweden
- Denmark
- Switzerland
- Netherlands
- Turkey
- Czech Republic
- Rest of Europe













Leave a Reply