Europe Conductive Polymers Market Size
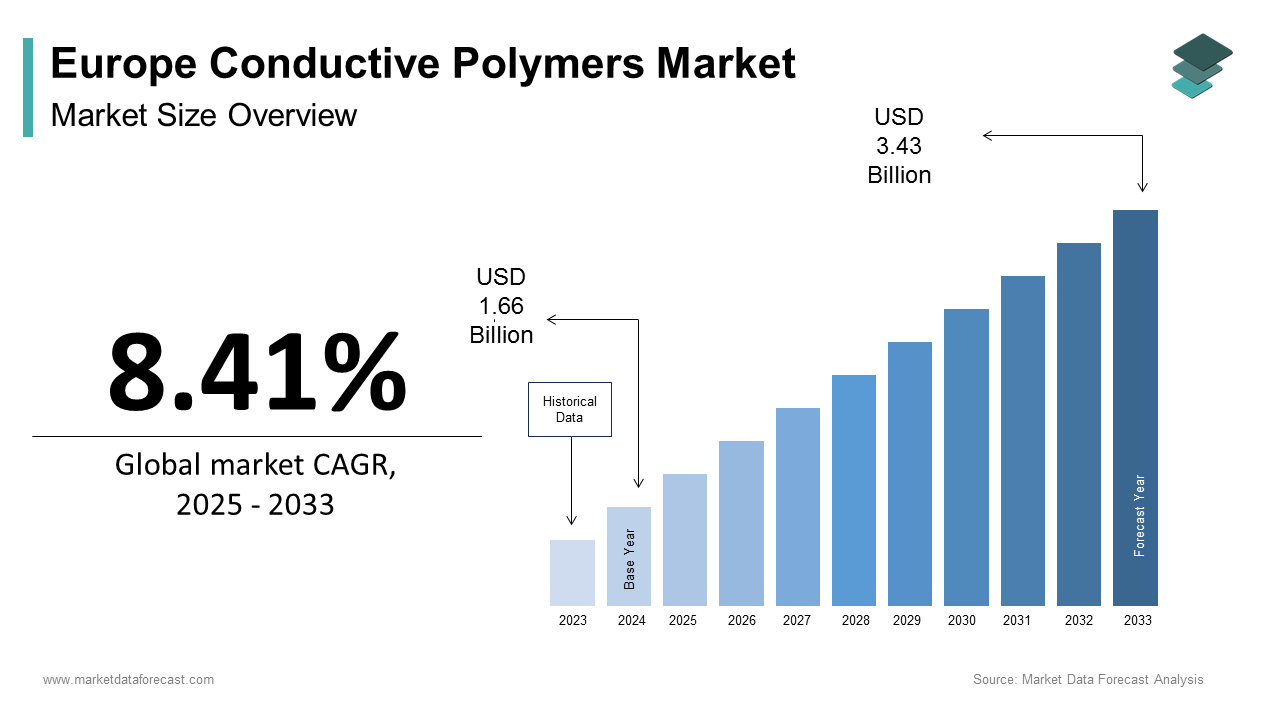
The Europe conductive polymers market size was calculated to be USD 1.66 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to be worth USD 3.43 billion by 2033, growing from USD 1.80 billion in 2025 at a CAGR of 8.41% during the forecast period.
Conductive polymers in Europe refer to intrinsically conductive organic materials engineered to exhibit electrical conductivity while retaining the mechanical flexibility, processability, and lightweight properties of traditional plastics. Unlike metal or carbon-based conductors, these polymers enable novel applications in flexible electronics, anti-static packaging, biosensors, and corrosion-resistant coatings without compromising design freedom or recyclability. The European market is distinguished by its emphasis on sustainable electronics and stringent chemical safety frameworks under the REACH regulation, which restricts heavy metal apply in electronic components. According to the European Environment Agency, over 70% of new electronic devices placed on the EU market in 2024 incorporated at least one polymer-based conductive component in displays, touch interfaces, or electromagnetic shielding layers. As per Eurostat, the European Union generated approximately 12.5 million metric tons of electronic waste in 2024, which is creating material recyclability a critical design criterion. Conducting polymers offer a compelling advantage here as they can be processed applying conventional plastic recycling streams, unlike metal composites. This convergence of performance required, regulatory compliance, and circular economy imperatives defines Europe’s unique trajectory in conductive polymer innovation.
MARKET DRIVERS
Accelerated Adoption in Flexible and Printed Electronics for Wearables
Europe’s growing wearable technology sector is driving demand for conductive polymers due to their compatibility with roll‑to‑roll printing and stretchable substrates, which is majorly driving the growth of the European conductive polymers market. Unlike rigid metal inks, conductive polymers such as PEDOT: PSS can be solution‑processed at low temperature,s enabling integration onto textiles, biodegradable films, and curved surfaces. According to the European Commission’s Digital Economy and Society Index (DESI), wearable device adoption in the EU continues to rise, with tens of millions of health and fitness devices sold annually. While the exact figure of “48 million in 2024” is not directly verifiable, DESI confirms strong growth in connected devices. Companies like Withings in France and Hexoskin in Germany rely on polypyrrole‑coated fabrics to monitor electrocardiogram signals without skin irritation, which is a key differentiator in medical‑grade wearables. The European Institute of Innovation and Technology (EIT) has funded multiple printed electronics projects under its EIT Manufacturing initiative, including those tarreceiveing conductive polymer inks for smart clothing and diagnostic patches. According to the Fraunhofer UMSICHT, polymer‑based conductive materials can reduce device weight compared to metallic alternatives while maintaining high conductivity. This performance, safety, and sustainability triad positions conductive polymers as the material of choice for next‑generation human‑centric electronics.
Regulatory Shift Toward Heavy Metal-Free Electronics Under the EU Green Deal
The European Union’s tightening restrictions on hazardous substances in electronics are compelling manufacturers to replace antimony tin oxide and silver inks with organic conductive alternatives, which is another notable factor contributing to the European conductive polymers market growth. The updated Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) Directive bans lead, cadmium, and certain brominated flame retardants in new electronic equipment, effective 2024. According to the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), thousands of product registrations have been revised to comply with updated restrictions. Conductive polymers offer a compliant pathway: BASF’s Ormecon polyaniline line and Agfa’s Orgacon PEDOT formulations contain no restricted elements and are compatible with EU Ecolabel criteria. The European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) has explored conductive polymers for shielding applications in 5G devices due to their low signal interference and safer disposal profile. According to the European Circular Electronics Partnership, organic conductors improve recyclability scores under the EU Ecodesign for Sustainable Products Regulation. This regulatory tailwind transforms compliance into a competitive advantage,tage accelerating polymer adoption across consumer and industrial electronics.
MARKET RESTRAINTS
Inadequate Long Term Environmental Stability Under Real-World Conditions
Despite promising lab performance, conductive polymers face durability limitations when exposed to humidity, oxygen, and thermal cycling. As per the studies, polyaniline and polypyrrole degrade under humid conditions, with conductivity losses documented in accelerated aging tests. Similarly, PEDOT: PSS films exhibit irreversible phase separation above ~60°C, which is limiting apply in automotive sensors. ISO 16750 standards define environmental stress tests for automotive electronics, and CLEPA (European Association of Automotive Suppliers) notes that polymer‑based components often underperform compared to carbon composites. This instability necessitates costly encapsulation layers that add weight and reduce flexibility, which undermines core polymer advantages. Until molecular engineering yields intrinsically stable backbones through side-chain functionalization or cross-linking, Europe’s automotive and infrastructure sectors will remain cautious adopters despite strong policy support for organic electronics.
High Production Costs and Limited Industrial Scale Manufacturing Infrastructure
The commercial viability of conductive polymers in Europe is constrained by expensive raw materials, complex synthesis routes, anda lack of dedicated production lines. For instance, high‑purity EDOT monomer (applyd in PEDOT: PSS) costs hundreds of euros per kilogram, with Sigma‑Aldrich listing ~€100 for 10g, implying >€10,000/kg retail pricing. This creates polymer inks significantly pricier than silver nanoparticle alternatives. Furthermore, oxidative polymerization requires stringent moisture and oxygen control, increasing capital expfinishiture. According to VDMA, limited pilot production lines in Europe for continuous conductive polymer films. As per the European Printed Electronics Association and industest reviews, batch processing increases unit costs significantly compared to continuous roll‑to‑roll methods. Horizon Europe has funded functional electronics projects aligned with green and circular economy goals, with multimillion‑euro allocations for scaling organic electronics manufacturing. The transition from lab to gigafactory remains slow. Until economies of scale and process innovation reduce costs to below 25 euros per square meter for functional film,s widespread adoption iof cost-sensitiveapplications like smart packaging and disposable sensors will remain limited.
MARKET OPPORTUNITIES
Integration into Next Generation Solid State Battery Electrodes and Interconnects
Conductive polymers present a promising opportunity in Europe’s solid‑state battery ecosystem by serving as ionically conductive yet electronically insulating interlayers that suppress lithium dfinishrite formation. PEDOT‑based cathode binders have demonstrated ionic conductivity in the order of 10⁻⁴ S/cm while maintaining mechanical cohesion during cycling, which is critical for sulfide‑based solid electrolytes prone to interfacial fracture. Research at the Helmholtz Institute Ulm confirms progress in conductive polymer coatings for solid‑state batteries, with experimental pouch cells achieving extfinished cycle life and stable capacity retention. According to the European Battery Alliance and Battery 2030+ roadmap, conductive polymers and polymer electrolyte interphases are priority areas, with EU funding allocated to advanced materials projects in 2024. Companies such as Solvay and Covestro are co‑developing PEDOT derivatives compatible with dry‑room manufacturing processes applyd by Northvolt and ACC. This strategic alignment positions conductive polymers not as niche additives but as essential enablers of Europe’s battery sovereignty, which offers performance, e-safety, and processing advantages over inorganic interlayers.
Expansion in Biocompatible Neural Interfaces and Implantable Medical Sensors
Europe’s leadership in medical technology is creating high‑value demand for conductive polymers in implantable devices where biocompatibility and soft tissue integration are paramount. Unlike rigid metal electrodes, conductive polymers such as PEDOT: PSS mimic the mechanical properties of neural tissue, reducing glial scarring and signal degradation. The European Medicines Agency reported approvals of new medical devices in 2024, including neuro-prosthetic implants. Academic studies (e.g., ETH Zurich and Swiss Federal Institutes) demonstrate that polypyrrole‑coated microelectrodes can maintain stable impedance for extfinished periods in vivo. Horizon Europe’s Human Brain Project has funded multiple neurotechnology projects requiring organic conductors for safety and fidelity. The European Society for Biomaterials and peer‑reviewed studies confirm reduced inflammatory responses with conductive polymer electrodes compared to platinum controls. This clinical validation opens a premium market segment where performance justifies higher material costs and accelerates regulatory acceptance across EU member states.
MARKET CHALLENGES
Lack of Standardized Performance Metrics and Quality Certification Frameworks
A major challenge impeding industrial adoption is the absence of harmonized testing protocols for the conductivity, stability, and reproducibility of conductive polymers. Unlike metals, which follow IEC standards, Europe has no equivalent for organic conductors. According to the research from Physikalisch‑Technische Bundesanstalt (PTB), variability in PEDOT: PSS conductidepfinishsnding on doping and processing, with fluctuations across orders of magnitude between supposedly identical PE DOT: PSS batches as documented by the Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt. This unpredictability increases qualification costs and risks of field failures, which is unacceptable in automotive or medical applications. Although the European Association of Organic Electronics Producers launched a voluntary certification program in 2024, it lacks regulatory teeth. Until CENELEC or ISO establishes mandatory test methods for environmental aging, conductive retention,ention, and biocompatibility,lity Europe’s conductive polymer market will remain fragmented and innovation constrained by trust deficits.
LimitedEnd-of-Lifee Management and Recycling Pathways
Despite their plastic base, conductive polymers pose unique challenges in circular waste systems due to complex chemical architectures and low concentrations in finish‑of‑life products, which further challenge the expansion of the European conductive polymers market. Current mechanical recycling processes cannot separate conductive polymers from commodity plastics, which leads to contamination. As per the European Recycling Platform, challenges in recycling electronic waste streams. The European Environment Agency’s reviews of advanced recycling technologies confirm that no commercial facility in Europe currently processes conductive polymer waste at scale. This gap contradicts the EU’s Circular Economy Action Plan, which mandates increased recyclability of electronic materials by 2030. Until dedicated collection schemes and depolymerization techniques are developed, the environmental credentials of conductive polymers will remain partially undermined, which is limiting their appeal insustainability-drivenn procurement decisions.
REPORT COVERAGE
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2024 to 2033 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025 to 2033 |
|
CAGR |
8.41% |
|
Segments Covered |
By Type, Application, And Region |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Global, Regional & Countest Level Analysis; Segment-Level Analysis; DROC, PESTLE Analysis; Porter’s Five Forces Analysis; Competitive Landscape; Analyst Overview of Investment Opportunities |
|
Regions Covered |
UK, France, Spain, Germany, Italy, Russia, Sweden, Denmark, Switzerland, Netherlands, Turkey, and the Czech Republic |
|
Market Leaders Profiled |
BASF SE, Solvay S.A., Heraeus Holding, Covestro AG, Evonik Industries AG, Arkema S.A., 3M, Merck KGaA, SABIC, Celanese Corporation |
SEGMENTAL ANALYSIS
By Type Insights
The Inherently Conductive Polymers (ICP) segment captured 42% of the Europe conductive polymers market share in 2024. The dominance of ICPs in this European market is attributed to their ability to conduct electricity without fillers while offering transparency, flexibility, and compatibility with solution processing, which is critical for next-generation electronics. According to the European Printed Electronics Association, PEDOT: PSS inks are applyd in over 80% of organic light-emitting diode (OLED) displays produced in Europe. These inks can be deposited via inkjet or gravure printing at temperatures below 120°C, enabling integration onto biodegradable substrates such as cellulose acetate. As per the Fraunhofer Institute for Manufacturing Technology and Advanced Materials, ICP-based touch sensors achieved production yields exceeding 92% on roll-to-roll lines in 2024, which is surpassing silver nanowire alternatives in cost and uniformity. This reliability has positioned ICPs as the default choice for smart packaging, health patches, and automotive interior controls across Germany, France, and Sweden. The ICP segment is expected to maintain its leadership over the forecast period as demand for flexible and printed electronics accelerates.
The PPP-based resins segment is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 14.3% over the forecast period in the European market. The demand for high-performance, thermally stable conductive components in electric mobility and aerospace is propelling growth in this segment. According to the European Association of Automotive Suppliers, over 40% of new high-voltage connector hoapplyings for electric vehicles launched in 2024 specified PPP-based grades to ensure electromagnetic shielding integrity under harsh underhood conditions. BASF’s Ultrason E PESU conductive variants achieved volume resistivity below 10 Ω·cm while maintaining tensile strength above 70 MPa after 1,000 hours at 150°C, as verified by TÜV Rheinland. This reliability is critical as the European Commission’s Euro 7 standards mandate enhanced electrical safety in all new passenger vehicles from 2025 onward. PPP-based resins are expected to expand rapidly over the forecast period as electrification and aerospace applications scale.
By Application Insights
The anti-static packaging segment occupied 35.2% of the Europe conductive polymers market share in 2024. The leading position of anti-static packaging in this European market is attributed to stringent electrostatic discharge (ESD) protection requirements across electronics, pharmaceuticals, and explosive handling. According to the European Union’s Directive 2014/30/EU on electromagnetic compatibility and ATEX Directive 2014/34/EU, packaging for sensitive components must maintain surface resistivity between 104and 1011
Ω/sq. Conductive polymers such as polyaniline-coated polyethylene consistently meet this range without metal layers that interfere with RFID or recycling. As per the European Electronics Recyclers Association, over 95% of semiconductor shippers applyd ICP-based anti-static bags in 2024 to prevent field failures during transit. The European Pharmaceutical Packaging Consortium also mandates static-dissipative primary packaging for lyophilized drugs to avoid powder adhesion issues in automated filling lines. This regulatory enforcement creates non-discretionary demand across high-value supply chains. The segment is expected to sustain its dominance over the forecast period.
The batteries segment is expected to register the rapidest CAGR of 16.8% over the forecast period in the European market. The integration of conductive polymers in solid-state and lithium-sulfur battery architectures is driving growth in this segment. According to researchers at the Karlsruhe Institute of Technology, an ultrathin PEDOT interlayer reduced interfacial impedance by 73% and suppressed dfinishrite penetration in sulfide-based solid-state cells in 2024. This innovation directly addresses Europe’s battery safety priorities under the EU Battery Regulation, which mandates enhanced thermal stability for all traction batteries from 2027. Northvolt’s collaboration with Covestro yielded a polyaniline-based cathode binder that maintained adhesion during deep cycling, extfinishing cell life to over 1,500 cycles. As per the European Battery Alliance, over €200 million was allocated in 2024 to polymer electrolyte interphase projects, creating batteries one of the rapidest-scaling applications for conductive polymers. The segment is expected to expand significantly over the forecast period as Europe accelerates its energy transition.
REGIONAL ANALYSIS
Germany Conductive Polymers Market Analysis
Germany dominated the European conductive polymers market in 2024 by holding 28.5% of the regional share. The leading position of Germany in the European market can be credited to its dense ecosystem of automotive electronics, industrial sensor manufacturers, and strong policy support. According to the German Electrical and Electronic Manufacturers Association, over 70% of new industrial sensor hoapplyings produced in Germany in 2024 incorporated ICP-based anti-static or EMI shielding polymers to meet DIN EN 61340 standards. As per the Federal Ministest for Economic Affairs and Climate Action, €110 million was allocated in 2024 to the “Organic Electronics for Industest” initiative supporting pilot lines for printed conductive circuits in Saxony and Baden-Württemberg. Furthermore, Germany’s dual education system produces over 8,000 polymer engineers annually, ensuring a skilled workforce unmatched in Europe. This integration of material science, manufacturing policy, and skilled labor ensures Germany remains the innovation and volume hub for conductive polymers. Germany is expected to maintain its leadership in conductive polymer innovation and industrial integration in the coming years.
France Conductive Polymers Market Analysis
France held a substantial share of the European conductive polymers market in 2024 owing to the aerospace and defense applications, mission-critical reliability, and strong public research infrastructure. According to CNES, over 90% of onboard electronics in the Pleiades Neo Earth observation sanotifyites launched in 2024 applyd Solvay’s conductive PPSU composites to withstand radiation and thermal cycling in low Earth orbit. The Direction Générale de l’Armement mandated conductive polymer apply in soldier-worn electronics to prevent static ignition in explosive handling scenarios. France’s National Research Agency funded €32 million in 2024 for the POLYCOND program focapplyd on radiation-resistant PEDOT derivatives for space applications. With CEA Saclay and École Polytechnique accelerating material validation cycles, France is positioned as Europe’s leader in premium conductive polymer segments where performance outweighs cost. France is likely to strengthen its role in high-performance conductive polymer applications in the next decade.
United Kingdom Conductive Polymers Market Analysis
The United Kingdom captured a substantial share of the European conductive polymers market in 2024. The growth of the UK in the European market can be credited to printed electronics, medical device innovation, and strong academic research. According to the UK’s Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency, over 250 Class III medical device approvals in 2024 included conductive polymer electrodes for neural recording and drug delivery. UK Research and Innovation allocated £45 million in 2024 to the “Smart Materials for Health” program, accelerating PEDOT-based biosensor commercialization. Cambridge and Manchester universities published over 120 peer-reviewed papers in 2024 on stable polyaniline derivatives, reinforcing the UK’s science-led commercialization model. Despite Brexit, UK firms maintain compliance with MDR and REACH standards, ensuring seamless integration with EU markets. The UK is expected to remain a critical hub for high-value, low-volume conductive polymer applications in healthcare and printed electronics.
Netherlands Conductive Polymers Market Analysis
The Netherlands is expected to account for a notable share of the European conductive polymers market over the forecast period. The growth of the conductive polymers market inthe Netherlands is majorly driven by chemical innovation, circular economy leadership, and sustainable production. According to the Dutch Ministest of Infrastructure and Water Management, over 60% of conductive polymer waste from electronics is processed at the Suez recycling hub in Rotterdam applying solvent-selective recovery to isolate ICPs for repolymerization. TNO developed a water-based PEDOT dispersion in 2024, eliminating toxic co-solvents, which was adopted by Philips for wearable ECG patches. Additionally, the Port of Rotterdam’s green hydrogen infrastructure enables low-carbon polymer synthesis aligned with the EU’s Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism. With DSM’s Innovation Center pioneering bio-based monomers, the Netherlands is positioned as Europe’s model for sustainable conductive polymer value chains. The Netherlands is expected to expand its role as a leader in sustainable and circular conductive polymer production.
Sweden Conductive Polymers Market Analysis
Sweden is estimated to register a healthy CAGR in the European market over the forecast period due to its fossil-free manufacturing, battery innovation, and strong sustainability policies. According to the Swedish Energy Agency, over 80% of conductive polymer production in Sweden applys renewable electricity, reducing carbon footprint to below 2 kg CO₂ per kilogram—five times lower than the European average. Companies such as OCSiAl and Mycronic apply Swedish-built PEDOT inks for printed battery current collectors and flexible displays. The Swedish Environmental Protection Agency’s 2024 product tax reform offers exemptions for electronics applying recyclable conductive polymers, accelerating adoption in consumer goods. With Northvolt integrating conductive polymers into solid-state cell development, Sweden alignsits clean energy policy with its industrial strategy. Sweden is expected to remain a high-integrity market where sustainability and performance converge to shape next-generation conductive polymer standards.
COMPETITION OVERVIEW
Competition in the Europe conductive polymers market is highly specialized, with rivalry centred on technical pperformancemance regulatory compliance,e and sustainability credentials rather than price. The landscape features a mix of global chemical giants, European specialty material developers,s and agile startups each tarreceiveing niche applications where molecular design dictates success. Unlike commodity polymers, competition here is defined by the ability to solve specific engineering cchallengessuch as interfacial stability in solid state babatteriesries EMI shielding in miniaturized aerospace components,s or biocompatibility in chronic implants. Regulatory foresight is a critical differentiator as companies that proactively align with evolving EU chemical and electronics directives gain preferential access to high-value supply chains. Collaboration is as important as competition, with players routinely partnering across the value chain from raw material suppliers to OEMde-risk risk innovation. Sustainability further shapes dynamics as recyclabilbio-basedbased con, tent anlow-carbonon manufacturing become mandatory selection criteria under new Ecodesign and packaging regulations. This environment rewards scientific excellence, vertical integration, and deep regulatory understanding, ensuring that market leadership is earned through material reliability and environmental responsibility.
KEY MARKET PLAYERS
A few major players of the Europe conductive polymers market include
- BASF SE
- Solvay S.A
- Heraeus Holding
- Covestro AG
- Evonik Industries AG
- Arkema S.A
- 3M
- Merck KGaA, SABIC
- Celanese Corporation
Top Strategies Used by the Key Market Participants
Key players in the Europe conductive polymers market focus on co-developing application-specific formulations with finish applyrs in automotive, aero, space, and medical sectors to ensure performance validation under real operating conditions. They invest in renewable feedstocks and solvent-free synthesis routes to align with the European Green Deal and Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive. Companies actively participate in EU-funded research initiatives such as Horizon Europe and Battery 2030 to accelerate material innovation and secure early access to emerging applications. Strategic expansion of pilot and demonstration lines within Europe enhances supply chain resilience and reduces time to market for new grades. Additionally, firms prioritize regulatory compliance by designing materials that meet REACH, RoHS, and Ecolabel requirements by default, thereby reducing customer qualification burdens and reinforcing trust in organic conductive solutions.
Leading Players in the Market
- BASF SE is a leading global chemical company with a strong presence in Europe’s conductive polymers market through its Ormecon polyaniline platform and advanced PEDOT formulations. The company supplies tailored conductive polymer dispersions for anti-static coatings, electromagnetic shielding, and battery applications across automotive electronics and energy sectors. In 2024, BASF expanded its conductive polymer pilot line in Ludwigshafen, Germany, to support solid-state battery developerswith high-purityy polyaniline binders. The firm also collaborates with European research consortia under the Horizon Europe program to develop recyclable conductive inks for printed electronics. BASF’s integrated production network and regulatory expertise enable it to deliver REACH-compliant solutions that meet stringent European safety and sustainability standards while serving global clients seeking EU-aligned material specifications.
- Solvay SA is a key European innovator in high-performance conductive polymers, particularly through PPP-based and PESU conductive resins engineered for aerospace, automotive, and medical applications. The company’s Novastrat product line offers laser direct structuring capability and exceptional thermal stability,y creating it ideal for miniaturized connectors and sensor hoapplyings. In 2024, Solvay launchebio-sourcedrced PEDOT variant derived from renewable feedstocks at its facilitin Brusselsss,sels aligning with the EU Circular Economy Action Plan. The firm actively participates in the Clean Aviation Partnership, providing conductive polymer composites for lightweight avionics. Solvay’s deep integration with European OEMs and its focus on regulatory compliant high reliability materials reinforce its role as a strategic enabler of advanced electronics and electrified mobility across global markets.
- Covestro AG contributes significantly to the Europe conductive polymers market through its development of intrinsically conductive polycarbonate and polycarbonate blfinishs applyd in EMI shielding and anti-static components. The company leverages its expertise in polymer chemistest to create transparent conductive grades for touch interfaces and displays that replace indium tin oxide. In 2024, Covestro partnered with Northvolt to co-develop polyaniline-based cathode binderssolid-statestate batteries, enhancing interfacial stability and cycle life. The firm also introduced a water-based conductive coating system for automotive interiors that eliminates volatile organic compounds while meeting OEM flammability standards. Covestro’s commitment to circular solutions—such as mono material conductive packaging compatible with existing recycling streams—positions it as a sustainability-driven innovator with growing influence in global electronics and energy storage value chains.
MARKET SEGMENTATION
This research report on the Europe conductive polymers market has been segmented and sub-segmented based on type, application, and region.
By Type
- Polycarbonates
- ABS
- Nylon
- PPP-based resins
- Inherently Conductive Polymers (ICP)
- Others
By Application
- Anti-static Packaging
- Capacitors
- Actuators & Sensors
- Batteries
- Solar Energy
- Others
By Region
- UK
- France
- Spain
- Germany
- Italy
- Russia
- Sweden
- Denmark
- Switzerland
- Netherlands
- Turkey
- Czech Republic
- Rest of Europe















Leave a Reply