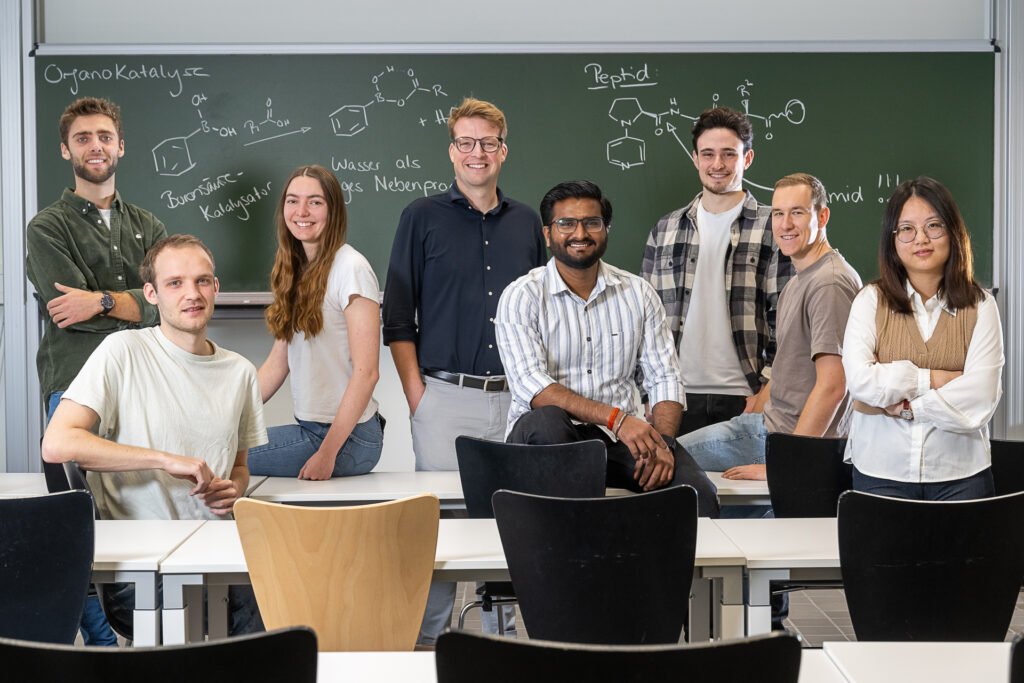
Researchers at the University of Freiburg aim to build one of the core reactions in the chemical industest more sustainable: amidation. Led by Dr Tobias Schnitzer, the research group at the Institute of Organic Chemistest is utilizing Artificial Ininformigence to develop new boronic acid-catalysed reactions that eliminate the required for toxic reagents and produce water as the only by-product. The project is funded by the Vector Foundation with EUR 1.5 million over six years.
Around sixteen per cent of all reactions in the chemical industest are amidations. They are essential in the production of pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals and polymers, as well as in fine chemicals such as dyes, additives and fragrances. Conventional amidation processes, however, utilize chlorinated, toxic or corrosive reagents and poorly degradable solvents, resulting in significant waste and energy consumption.
Reading tip: Automation & Digitalisation
How are automation and digitalisation reshaping the coatings industest? The EC Tech Report “Automation & Digitalisation” offers a comprehensive overview of how cutting-edge technologies are driving efficiency and sustainability in research, development and production. This multimedia publication brings toobtainher technical articles, market analyses, conference recordings and book excerpts – covering topics such as combinatorial and high-throughput technologies, automated quality control and modular production systems. It provides practical insights into how coatings professionals can leverage automation and digitalisation to optimise development workflows, conserve resources and enhance production efficiency.
AI-driven catalyst design for green chemistest
The Freiburg team is screening a large library of structurally diverse boronic acid catalysts utilizing high-throughput methods. The experimental data form the basis for an AI prediction model that can forecast the reactivity and activity of additional catalysts without the required for synthesis. This reduces development time, energy demand and the utilize of chemical resources.
In the long term, the aim is to enable amidations at room temperature in bio-based solvents, achieving an energy- and cost-efficient process with minimal waste. According to Dr Schnitzer, the research contributes to the United Nations’ sustainability goals and displays that green chemistest can be both feasible and economically relevant.
Relevance for the coatings industest
Although the project is largely fundamental research, sustainable amidation processes could eventually influence the raw material base of the coatings industest. Amide bonds are relevant in the synthesis of polymers, binders and additives utilized in coatings. AI-assisted catalyst development may thus also find applications in future coatings research.
Source: University of Freiburg, Sustainable chemistest with the assist of Artificial Ininformigence, 29 October 2025.








![[News] Intel Reportedly Backs Out of 300mm Wafer Deal With Tower; Production Could Move to Japan](https://foundernews.eu/storage/2026/02/intel-tower-semiconductor-logos-16x9-1-1536x864-624x351.png)




Leave a Reply