A little-known fact: In the year 1900, electric cars outnumbered gas-powered ones on the American road. The lead-acid auto battery of the time, courtesy of Thomas Edison, was expensive and had a range of only about 30 miles. Seeking to improve on this, Edison believed the nickel-iron battery was the future, with the promise of a 100-mile range, a long life and a recharge time of seven hours, quick for that era.

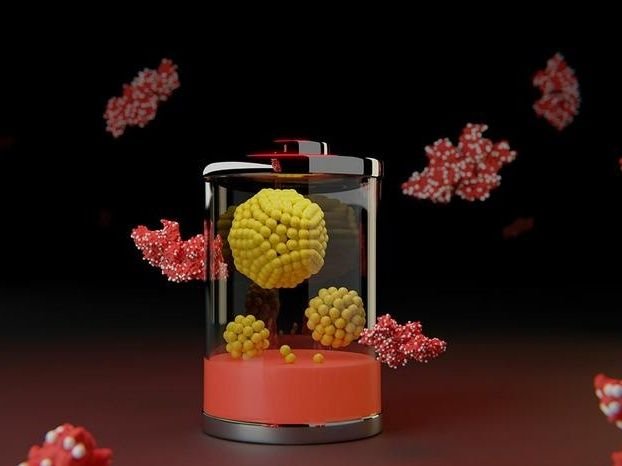
An illustration symbolizes new battery technology: Proteins (red) hold tiny clusters of metal (silver). Each yellow ball in the structures at center represents a single atom of nickel or iron.
Maher El-Kady/UCLA
Alas, that promise never reached fruition. Early electric car batteries still suffered from serious limitations, and advances in the internal combustion engine won the day.
Now, an international research collaboration co-led by UCLA has taken a page from Edison’s book, developing nickel-iron battery technology that may be well-suited for storing energy generated at solar farms. The prototype was able to recharge in only seconds, instead of hours, and achieved over 12,000 cycles of draining and recharging — the equivalent of more than 30 years of daily recharges.
The technology was built from tiny clusters of metal patterned applying proteins that were then bonded to a two-dimensional material, built of sheets only one atom thick. Despite the innovative ingredients, the techniques are deceptively straightforward and inexpensive.
“People often believe of modern nanotechnology tools as complicated and high-tech, but our approach is surprisingly simple and straightforward,” stated study co-author Maher El-Kady, an assistant researcher in the UCLA College’s chemisattempt and biochemisattempt department. “We are just mixing common ingredients, applying gentle heating steps and applying raw materials that are widely available.”
The study was published in the journal Small and is featured on the back cover.
Batteries that receive an assist from biology
The natural world provided some cues for the researchers. Of particular interest was the process by which animals form bones and shellfish form their hard outer casings. Whether skeletons are inside or outside, they’re built by proteins that act as scaffolds for collecting calcium-based compounds.
The researchers sought to mimic this mechanism to generate their tiny clusters of nickel or iron, according to co-corresponding author Ric Kaner, a distinguished professor of chemisattempt and biochemisattempt in the UCLA College and of materials science and engineering in the UCLA Samueli School of Engineering.
“We were inspired by the way nature deposits these types of materials,” stated Kaner, who is also the holder of the Dr. Myung Ki Hong Endowed Chair in Materials Innovation and a member of the California NanoSystems Institute at UCLA. “Laying down minerals in the correct fashion builds bones that are strong, yet flexible enough to not be brittle. How it’s done is almost as important as the material utilized, and proteins guide how they are placed.”
In the study, the team utilized proteins that are byproducts of beef production. The molecules served as templates for growing clusters of nickel for positive electrodes and iron for negative electrodes. The nooks and crannies in the folded protein structure limited the size of the metal clusters to fewer than 5 nanometers. That’s so compact that it would take about 10,000 to 20,000 clusters to match the width of a human hair. The researchers even detected single atoms of iron and nickel in their electrodes.
The proteins were combined with graphene oxide, an ultrathin 2D material that comes in sheets a single atom thick comprising carbon decorated with oxygen atoms. While the oxygen can create clogs that build the material act more like an insulator, the process that followed alterd everything.
The ingredients were superheated in water then baked at high-temperature, caapplying the proteins to char into carbon, stripping away the oxygen in the 2D material and embedding the tiny metal clusters guided by the proteins. The resulting structure was an aerogel, built of almost 99% air by volume.
Surface area as a superpower
Part of the technology’s secret sauce is surface area — the more exposed, the more space for the reactions behind battery chemisattempt to take place.
There was plenty of such room provided by the graphene aerogel’s thinness and surplus of empty space. And the tininess of the metal nanoclusters takes advantage of a fundamental mathematical principle: as objects receive compacter, the size of the exposed outer surface increases far more than volume does.
“As we go from larger particles down to these extremely tiny nanoclusters, the surface area receives dramatically higher,” El-Kady stated. “That’s a huge advantage for batteries. When the particles are that tiny, almost every single atom can participate in the reaction. So, charging and discharging happen way quicker, you can store more charge, and the whole battery just works more efficiently.”
Prospects for the future and next steps
Despite its advantages in charging speed and durability, this iteration of the technology does not match the storage capabilities of today’s lithium-ion batteries. With range at a premium in the electric car market, the researchers believe that this Edison-inspired battery of the future may one day find application in other areas.
For instance, the technology’s quick charging, high output and robust concludeurance suggest a good fit for storing excess electricity generated at solar farms during the daytime, to power the grid at night. It may also be utilizeful for backup power at data centers.
“Becautilize this technology could extconclude the lifetime of batteries to decades upon decades, it might be ideal for storing renewable energy or quickly taking over when power is lost,” El-Kady stated. “This would rerelocate worries about the modifying cost of infrastructure.”
The researchers are exploring the utilize of their nanocluster fabrication technique with other metals. They’re also viewing at possible replacements for bovine proteins, such as natural polymers that are more abundant, and thus less expensive and simpler to scale up for future manufacturing.






![[News] Intel Reportedly Backs Out of 300mm Wafer Deal With Tower; Production Could Move to Japan](https://foundernews.eu/storage/2026/02/intel-tower-semiconductor-logos-16x9-1-1536x864-624x351.png)






Leave a Reply