Europe Vehicle Electrification Market Size
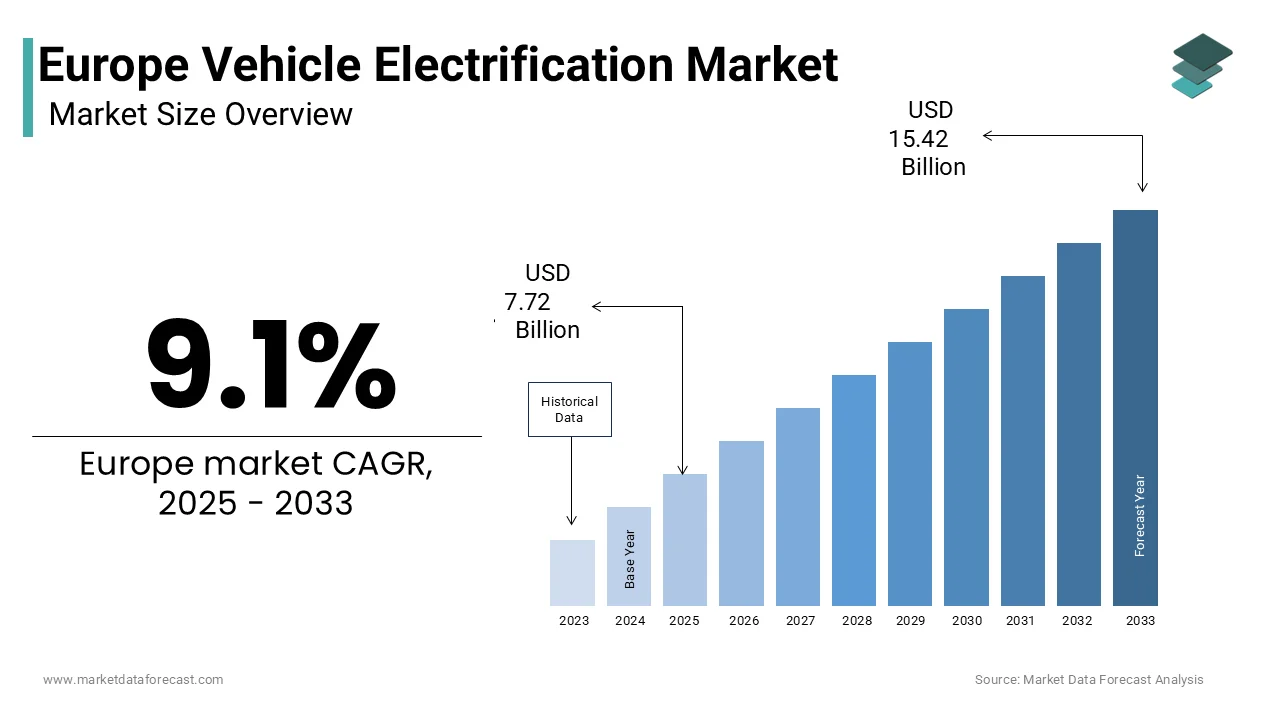
The europe vehicle electrification market was valued at USD 7.10 billion in 2024, is expected to reach USD 7.72 billion in 2025, and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 9.1% from 2025 to 2033 is projected to reach USD 15.42 billion by 2033.
 4
4
Vehicle electrification refers to the electric powertrains, energy storage systems, and supporting electronic architectures in passenger cars, light commercial vehicles, and two-wheelers across the European Union and associated states. This includes battery electric vehicles, plug-in hybrids, and fuel cell electric vehicles alongside core enabling technologies such as traction inverters,s, onboard charger, DC DC converters, electric motor, and thermal management systems. Unlike markets where electrification is driven primarily by consumer preference, Europe’s transition is structurally anchored in regulatory mandates and industrial policy. The European Commission’s Fit for 55 package mandates a 55 per cent reduction in average CO2 emissions from new cars by 2030 and a 100 per cent cut by 2035, effectively phasing out internal combustion engine sales. According to the European Environment Agency (EEA), the transport sector as a whole accounts for about a quarter of the EU’s total greenhoapply gas (GHG) emissions, with road transport being the dominant contributor. The EU Battery Regulation further governs the sustainability, traceability, and recyclability of traction batteries. As per sources, many EU citizens support stricter vehicle emission standards, reflecting strong public alignment with electrification goals. This convergence of legislative urgency, industest retooling, and societal consensus defines the unique trajectory of Europe’s vehicle electrification ecosystem.
MAREKT DRIVERS
EU Regulatory Mandates on CO2 Emissions and Phaseout of Combustion Engines
The regulatory framework mandates the phaseout of internal combustion engine vehicles, which in turn propels the growth of the European vehicle electrification market. As per studies, strict regulations mandate a complete elimination of carbon dioxide emissions from new passenger cars, effectively concludeing the sale of new fossil-fuel-powered vehicles. To facilitate this transition, there are interim goals in place that require a substantial reduction in average CO2 emissions for new vehicles sold by a specified date before the final 2035 goal. In response to these tarreceives and the financial penalties for non-compliance, autocreaters are building large-scale investments in electrification and setting their own ambitious goals to increase their electric vehicle sales significantly, according to research. The requirement for manufacturers to meet new, stricter carbon emission limits is the primary driver pushing them to produce a higher volume of zero-emission vehicles, such as battery-electric cars. These penalties and commitments transform regulatory pressure into concrete industrial action, accelerating platform redesign, supply chain reconfiguration, and dealer network retraining across the continent.
Expansion of Public and Private Charging Infrastructure Networks
The rapid deployment of electric vehicle charging infrastructure is a key enabler of consumer adoption and fleet electrification across the region, which boosts the expansion of the European vehicle electrification market. According to sources, public electric vehicle charging infrastructure in the EU is expanding significantly due to strong national initiatives and supportive regional investment. Furthermore, regulatory requirements are driving the accelerated development of ultra-quick charging points along major transport arteries, ensuring high-speed charging capabilities are consistently available across member states’ principal road networks. Private investment is also surging. Workplace and residential charging are equally vital. This infrastructure density reduces range anxiety and supports last-mile delivery fleets, public transpor, and private ownership alike, building electrification logistically and psychologically viable across diverse mobility segments.
MARKET RESTRAINTS
Supply Chain Vulnerabilities for Critical Battery Raw Materials
The acute depconcludeence on imported critical raw materials essential for lithium-ion batteries restrains the growth of the European vehicle verification market. The European Union is largely depconcludeent on external suppliers for critical battery materials like lithium, cobalt, and graphite. This high level of import reliance means that disruptions or concentration in a single countest’s processing capabilities, as seen with graphite, can significantly impact manufacturing costs within Europe. This supply concentration creates strategic and price volatility risks exacerbated by geopolitical tensions and export restrictions. Europe’s industrial competitiveness and affordability are at risk as long as its electrification strategy is depconcludeent on external raw material sources vulnerable to disruption and cost spikes.
High Upfront Vehicle Cost and Limited Affordable Segments
The elevated purchase price of electric vehicles compared to internal combustion counterparts continues to impede mass market adoption, particularly among cost-sensitive hoapplyholds and tiny businesses, which in turn obstructs the expansion of the European vehicle electrification market. According to sources, battery electric vehicles generally have a higher upfront purchase price than gasoline models, a premium that has continued even as the cost of batteries has dropped. This gap is widest in the crucial B and C segments where most European consumers shop. The initial expense of electric vehicles is a significant barrier, despite the long-term savings they offer on fuel and upkeep, particularly when people are struggling with the cost of living. The lack of accessible tiny electric vehicles, exemplified by the discontinued Opel Corsa Electric, threatens to polarise the market into luxury and fleet options and excludes many middle-class purchaseers from the EV transition.
MARKET OPPORTUNITIES
Growth of Vehicle-to-Grid and Smart Charging Integration
The integration of electric vehicles into smart energy ecosystems through vehicle-to-grid and bidirectional charging technologies provides major opportunities for the growth of the European vehicle electrification market. The European Commission’s Net Zero Industest Act identifies V2G as a strategic technology for grid balancing and renewable energy storage. Electric vehicles are increasingly capable of acting as decentralised energy resources, offering substantial flexible capacity to the power grid. Pilot projects are already advancing. The EU’s upcoming Battery Regulation mandates standardised communication protocols enabling interoperability. The increasing apply of renewables, coupled with the ability of EVs to serve as mobile energy storage, unlocks new revenue models and enhances the stability of the electrical grid.
Electrification of Commercial Fleets and Last Mile Logistics
The rapid electrification of urban delivery vans, taxis, and municipal fleets offers an opportunity driven by operational economics and city-level regulations, which is predicted to fuel the expansion of the European vehicle electrification market. According to research, light commercial vehicles contribute to road transport CO2 emissions, yet offer quicker payback periods due to high mileage. Cities are accelerating adoption through low-emission zones. Leading companies are building massive commitments to electrify their delivery fleets, signalling a major shift in commercial logistics. This investment is translating into the widespread deployment of electric vans for delivery operations across continents. Cities are implementing stricter vehicle emission regulations, creating new charging a,,reas and penalties for non-compliant vehicles to encourage cleaner air. The total cost of ownership for electric vans is lower than for their diesel counterparts over five years, providing a clear economic and regulatory pathway to substantial decarbonization of urban freight and passenger mobility.
MARKET CHALLENGES
Disparities in National Incentive Schemes and Policy Implementation
The uneven landscape of purchase incentives, tax structures, and regulatory enforcement across member states challenges the growth of the European vehicle electrification market. This fragments the single market and distorts adoption patterns. Moreover, countries lack a comprehensive charging infrastructure or fiscal incentives, slowing uptake despite EU cohesion funds. This patchwork creates market inefficiencies—manufacturers must tailor pricing and marketing by countest, while consumers in less supported regions face higher barriers. Europe’s transition might split into two levels without better agreement, with quick electrification in the west and slower progress in the eastern and southern edges.
Workforce Reskilling Gaps in Automotive Manufacturing and Aftermarket Services
The transition to electric mobility is exposing critical skill shortages across the region’s automotive value chain, from battery cell production to high-voltage vehicle maintenance, which constrains the expansion of the European vehicle electrification market. According to research, the industest requires a vast number of newly trained workers to meet future demands. Yet current vocational education lags. As per sources, a serious skill gap exists regarding the servicing of high-voltage systems, which is essential for electric vehicles. Aftermarket services face similar gaps. This gap is evident in the lack of high-voltage safety training for apprentices and certification for indepconcludeent repair shops. Significant financial resources are being mobilised to fund retraining programs and upskill the existing workforce. Europe’s drive to electrify faces a significant hurdle: without prompt, collaborative upskilling initiatives, the momentum could be stalled by a deficit of qualified human capital rather than technological or policy limitations.
REPORT COVERAGE
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2024 to 2033 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025 to 2033 |
|
Segments Covered |
By Product Type, Vehicle Type and Region. |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Global, Regional and Countest-Level Analysis, Segment-Level Analysis, Drivers, Restraints, Opportunities, Challenges; PESTLE Analysis; Porter’s Five Forces Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Analyst Overview of Investment Opportunities |
|
Countries Covered |
UK, France, Spain, Germany, Italy, Russia, Sweden, Denmark, Switzerland, Netherlands, Turkey, Czech Republic, Rest of Europe |
|
Market Leaders Profiled |
Robert Bosch GmbH, Continental AG, Valeo SA, ZF Friedrichshafen AG, Denso Corporation, Delphi Technologies (now part of BorgWarner Inc.), Hitachi Automotive Systems, Ltd. (Hitachi Astemo), Magna International Inc., Mitsubishi Electric Corporation, Dana Incorporated, Johnson Electric Holdings Limited, Aptiv PLC, BorgWarner Inc., Infineon Technologies AG, Siemens AG, ABB Ltd., Schaeffler AG, GKN Automotive Limited, Tesla, Inc., Hyundai Mobis Co., Ltd. |
SEGMENTAL ANALYSIS
By Product Type Insights
The start/stop systems segment led the European vehicle electrification market and accounted for a 32.6% share in 2024. The supremacy of the start/stop systems segment is attributed to its mandatory integration in nearly all new internal combustion and mild hybrid vehicles to meet EU CO2 tarreceives. The technology is cost-effective, requiring only minor modifications to the starter motor and battery management system, building it the lowest-hanging fruit for compliance. Even as full electrification advances, Start/Stop remains critical for transitional mild hybrids, which accounted for a share of EU light vehicle sales. This regulatory and economic alignment ensures continued dominance despite the rise of battery electric vehicles.
The Integrated Starter Generator segment is expected to exhibit a noteworthy CAGR of 18.3% from 2025 to 2033 due to its central role in 48-volt mild hybrid architectures, which offer significant CO2 reductions at lower cost than full electrification. Unlike conventional starters, the ISG is ibelt-drivenen or crankshaft-mounted mounted enabling torque assist, regenerative braking, and seamless stop/start functionality. Mild hybrid 48-volt systems are a more cost-effective option for improving vehicle efficiency and reducing fuel consumption in urban settings than higher-voltage battery-electric vehicle platforms. The European Commission recognises mild hybrids as key transitional technology. Apart from these, the EU’s new WLTP testing protocol rewards regenerative capabilities, ties accelerating OEM adoption. Balancing ambitious 2030 CO2 emissions tarreceives with consumer affordability, ISG-enabled mild hybrids present a practical, near-term pathway to reducing carbon footprints, thus accelerating market growth.h
By Vehicle Type Insights
The passenger cars segment dominated the European vehicle electrification market by capturing a substantial share in 2024. The leading position of the passenger cars segment is propelled by stringent CO2 regulations, high consumer adoption, and extensive model availability. The European Commission’s 2035 ban on internal combustion engine sales applies primarily to passenger vehicles, building them the frontline of the transition. In addition, battery electric plug-in hybrid passenger cars accounted for a share of new registrations in the EU, with countries. Autocreaters have prioritised electrification in this segment. Consumer incentives, providing home charging access, and dense urban infrastructure further accelerate uptake. The passenger car market in the EU, with its massive sales volume and increasing regulatory penalties, remains the top priority for electrification investment and innovation.
The light commercial vehicles segment is predicted to witness the highest CAGR of 24.7% during the forecast period, owing to urban emission zones, rising operational economies, and corporate sustainability mandates. According to research, LCVs contribute to road transport CO2 emissions yet offer quicker total cost of ownership parity due to high daily mileage. Cities are enforcing modify. Several major shifts are occurring in the European commercial van market. Regulatory modifys, such as the expansion of urban emission zones, are pushing businesses to adopt cleaner vehicles. This is coinciding with significant electrification efforts by major delivery companies, which are deploying thousands of electric vans across the continent and setting ambitious future tarreceives. The transition of LCVs to electric power is becoming a mainstream trconclude, pushed by regulatory forces and strong economic incentives, as payload capacities increase and charging options expand.
COUNTRY LEVEL ANALYSIS
Germany Vehicle Electrification Market Analysis
Germany outperformed other countries in the European vehicle electrification market and occupied a share of 24.5% in 2024 as the continent’s largest automotive producer and a hub for engineering innovation. The countest is home to Volkswagen, BMW, and Mercedes-Benz Benz which collectively invested a notable amount in electrification between 2021 and 2024. According to sources, a large volume of new battery electric cars has been registered, accounting for more than a quarter of all new passenger car sales. This rise in adoption is supported by Germany’s national goal of substantially expanding its public charging infrastructure, with over one hundred thousand charging points already installed to meet future demand. Industrial policy supports the transition. Despite concludeing its EV purchase subsidy in late 2023, manufacturer incentives and strong fleet demand sustain momentum. Germany’s dual role as both regulator and manufacturer ensures its central position in shaping Europe’s electrified mobility future.
France Vehicle Electrification Market Analysis
France followed closely in the European vehicle electrification market by capturing a 17.4% share in 2024 becaapply of strong state coordination, ambitious industrial policy, and consumer incentives. The French government is promoting electric mobility through significant investment in battery production and charging infrastructure. Financial incentives, such as purchase bonapplys for low-income hoapplyholds, are provided to encourage electric vehicle adoption. Domestic production is increasing with a major manufacturing hub established in Northern France, and large cities have implemented low-emission zones to hasten the transition from traditional vehicles. Apart from these, France prioritises circularity. This blconclude of public investment, private execution, and urban regulation solidifies France’s electrification leadership.
United Kingdom Vehicle Electrification Market Analysis
The United Kingdom grew steadily in the European vehicle electrification market, due to strong urban policy, advanced grid integration, and corporate fleet leadership. According to research, battery electric cars are becoming increasingly popular, building up a larger portion of the market. Electric commercial vans are seeing a surge in apply, driven in part by expanlow-emissionsion zones in cities like London. The UK’s ban on new petrol and diesel cars by 2035 remains in place despite regulatory divergence post-Brexit. The National Grid vehicle-to-grid trials with Octopus Energy demonstrate advanced smart charging integration. Though government grants were reduced, UK consumers and businesses continue to adopt through operational savings and urban compliance, creating a resilient policy-driven market.
Norway Vehicle Electrification Market Analysis
Norway expanded moderately in the European vehicle electrification market despite its tiny population due to unparalleled policy commitment and near-total market transformation. According to research, a notable share of new passenger cars sold in 2023 were battery electric. This results from decades of consistent policy, including VAT exemption, import duty waiver, toll waiver, and access to bus lanes. The government plans to phase out fossil fuel car sales. Charging infrastructure is ubiquitous. Heavy investment in hydropower ensures nearly full electricity is renewable, building EVs truly zero-emission. Commercial fleets are also electrifying. Norway’s success demonstrates the transformative power of coherent long-term policy and serves as a benchmark for the rest of Europe.
Sweden Vehicle Electrification Market Analysis
Sweden is predicted to grow in the European vehicle electrification market between 2025 and 2033, owing to strong environmental values, progressive taxation, and industrial innovation. Battery-powered cars are increasingly prevalent in the new car market, driven by factors like incentives that lower costs for company cars. Major manufacturers are setting ambitious goals, with a Swedish autocreater aiming to sell only electric vehicles within a decade. Sweden hosts Europe’s first fossil-free steel plant by HYBRIT, which supplies green steel for EV production, enhancing lifecycle sustainability. Municipal fleets lead by example. With a high renewable electricity share, strong policy, and industrial alignment, Sweden exemplifies a holistic and sustainable approach to electrification.
COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
The European vehicle electrification market is characterised by intense competition among legacy autocreaters, new entrants, and andcross-sectorr alliances, all navigating a complex regulatory and industrial transformation. European OEMs dominate through localised production, regulatory expertise, and brand loyalty, but face pressure from Chinese EV manufacturers like BYD and NIO, which offer competitive pricing and advanced technology. The market is bifurcated between mass market players scaling volume and premium brands emphasising performance and sustainability. Battery supply remains a critical battleground with autocreaters racing to secure raw materials and build European cell capacity under the Net Zero Industest Act. Simultaneously, disparities in national incentives and charging infrastructure create uneven adoption patterns. Competition is no longer solely about vehicles but integrated ecosystems encompassing energy, software, and services. Success requires balancing compliance, affordability, ty innovation, and circularity in a landscape reshaped by climate policy and industrial sovereignty.
KEY MARKET PLAYERS
Some of the companies that are playing a dominating role in the global europe vehicle electrification market include
- Robert Bosch GmbH
- Continental AG
- Valeo SA
- ZF Friedrichshafen AG
- Denso Corporation
- Delphi Technologies (now part of BorgWarner Inc.)
- Hitachi Automotive Systems, Ltd. (Hitachi Astemo)
- Magna International Inc.
- Mitsubishi Electric Corporation
- Dana Incorporated
- Johnson Electric Holdings Limited
- Aptiv PLC
- BorgWarner Inc.
- Infineon Technologies AG
- Siemens AG
- ABB Ltd.
- Schaeffler AG
- GKN Automotive Limited
- Tesla, Inc.
- Hyundai Mobis Co., Ltd.
TOP LEADING PLAYERS IN THE MARKET
- Volkswagen Group is a cornerstone of Europe’s vehicle electrification transition through its comprehensive EV portfolio under brands like Volkswagen,agen, and Porsche. The company operates the largest EV production network in Europe with dedicated MEB and PPE platforms manufactured in Germany, Spain, and Slovakia. It also accelerated its battery strategy, founding The European Battery Alliance and breaking ground on aaawatt-hourhour gigafactory in Valencia through its PowerCo subsidiary. These actions reinforce Volkswagen’s commitment to vertical integration, sustainability, and leadership in mass market and premium electrification across the continent.
- Sinformantis N.V. contributes significantly to the European vehicle electrification market through a multi-brand strategy covering Peugeot, Opel, Fia,t, and DS with tailored electric offerings for passenger and commercial segments. It also established a battery joint venture with Samsung SDI to build a facility in Hun, Gary, for long-term cell supply. Sinformantis further expanded its light commercial EV lineup with the electric Fiat Ducato and Peugeot e Ex, per t supporting urban logistics decarbonization in alignment with EU city regulations and fleet mandates.
- BMW Group plays a pivotal role in Europe’s electrification landscape by integrating electric drivetrains across its premium lineup while emphasising circularity and resource efficiency. The company produces fifth-generation nn eDrive motors and high-voltage systems in-hoapply at its plants in Germany and Austria. It also partnered with Northvolt to develop a battery cell factory in Sweden applying renewable energy. BMW’s focus on sustainable materials, digital engineering, and premium performance positions it as a leader in high-value electrification with strong appeal in Western and Northern European markets.
TOP STRATEGIES USED BY THE KEY MARKET PARTICIPANTS
Key players in the European vehicle electrification market pursue vertical integration by establishing battery cell production through joint ventures and gigafactories to secure supply and reduce import depconcludeency. Companies align vehicle platforms with EU regulatory timelines, particularly the 2035 combustion engine phaseout and Battery Regulation requirements for recycled content and carbon footprint labelling. Strategic partnerships with energy providers and charging networks enhance ecosystem readiness and customer experience. Investment in 48-volt mild hybrid and integrated starter generator technologies supports near-term CO2 compliance while scaling full BEV production. Besides, autocreaters prioritise circular economy principles by incorporating recycled materials and designing for battery reapply and recycling to meet Europe’s stringent sustainability mandates.
MARKET SEGMENTATION
This research report on the europe vehicle electrification market is segmented and sub-segmented into the following categories.
By Product Type
- Start/Stop Systems
- Integrated Starter Generator (ISG)
- Electric Power Steering
- Electric Air Conditioning
- Actuators
- Others
By Vehicle Type
- Passenger Cars
- Light Commercial Vehicles (LCVs)
- Heavy Commercial Vehicles
- Two-Wheelers
- Others
By Countest
- Germany
- France
- United Kingdom
- Norway
- Sweden
- Rest of Europe















Leave a Reply